Body Composition
Health-Related Component: Body Composition
Overview
Body composition is the proportion of fat & fat-free mass (muscles, ligaments, water, bone, organs) in the body. The relationship between fat and muscle in the body is important to have a low body fat percentage. A body composition with more muscle mass in the body reduces the risk of diabetes, heart problems, and inflammation in the body. The inflammation tends to be the root of most problems in the body that gets worse over time.
Fat Mass
When looking at the image above, you’re looking at a pound of fat mass compared to a pound of muscles. The fat mass is much bigger and wider. It takes up a lot more space and area in the body. You can see how this can cause a lot of stress to the bones, muscles & joints. The leaner you are the less stress and damage you will do to the body. Goodbye hip and knee replacements. Now, I’m definitely not saying that all fat mass is bad as we still need fat mass for storage and other uses in the body(The Functions of Fats in the Body | Eufic). The notion here is that too much of anything is never a good time so keep it in mind. We do want to stay within a healthy body fat percentage range.
Fat-Free Mass
Fat-free mass is what we more commonly know as muscle. This is what we are aiming to build and develop for our health. Without this, you won’t be able to sustain your body weight or move in any way. It doesn’t have as much volume but it still takes up space in the body. Fat-free mass also helps boost metabolism which is how the body uses energy (food we eat) to produce heat. We wouldn’t be able to survive without any fat-free mass at all.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
The body mass index is an okay way of understanding what healthy body weight is for any person, yet it has its problems. It uses height and weight to calculate the number that you see on your doctor’s scale (if they have one). Underweight is considered a BMI less than 18.5, the normal range is between 18.5-25, overweight is from 25-30, obesity starts at 30-40, and severe obesity starts at 40+.
There are better ways to measure body composition than BMI?
I pride myself on giving you information, showing different perspectives, and allowing you to come to your own conclusion. What's my issue with the body mass index to measure body composition? It's not specific enough. Let's use an example here. Client A is 6'0 and 230 pounds. He's muscular and is on a healthy diet and exercise regime. Client B is also 6'0 and 230 pounds but does not take care of his health and is out of shape. Based on the BMI calculation both clients' BMI is 31. That's technically obese. If we look at both clients side by side, that would not be the case for client A.
With that being said, BMI is a number to put into consideration yet we want to go deep and look at the ratio of fat-free mass (muscle mass) & fat in the body.
Measure Your Body Composition
When measuring body composition, we will be looking at the percentage of body fat. When working on your health and fitness, no matter if you're working on gaining muscle or weight loss, we look for progress. Progress in weight loss by seeing a change in the percentage of muscle mass and body fat. With that in mind, what are the healthy percentages for body fat?
When looking at the image above, you’re looking at a pound of body fat compared to a pound of muscles. The body fat is much bigger and wider. It takes up a lot more space and area in the body. You can see how this can cause a lot of stress to the bones, muscles & joints. The leaner you are the less stress and damage you will do to the body. Goodbye hip and knee replacements. Now, I’m definitely not saying that all body fat is bad as we still need body fat for storage and other uses in the body. The notion here is that too much of anything is never a good time so keep it in mind. We do want to stay within a healthy body fat percentage range.
Body Fat Percentage: Healthy Ranges
Now we have a low minimum for essential body fat and the range for healthy body fat. When discussing essential body fat, this has to do with having the least amount of body fat for the body to perform bodily functions. The healthy body fat range is what’s allowed in the body where you are at low risk for any of the diseases mentioned in the paragraph above.
Essential fat % is typically around 2–5% for men, 10–13% for women (due to their breasts and the need for childbearing).
The healthy range of body fat for men is typically between 8–19% for men and 21–33% for women.
Body Fat Percentage Charts
How Do I measure my body fat?
Now the question comes up, how do I measure body fat percentages? There are several ways to measure body fat percentage. Now, these three methods are not 100% accurate. One of the three below will do just fine to allow you to get the information you need to move forward with creating a plan to improve your health and wellness.
1) Skinfold calipers
This method of measuring has been used to estimate body fat for over 50 years (PubMed). You’re measuring the thickness of the body fat at certain locations of your body. The locations do vary for men and Women. There are options to do 3 or 7 site measurements.
The 3 site measurements for men are the chest, abdomen & thigh or the chest, triceps & area beneath the scapula (PubMed). For women, it is the triceps, above the hip bone & either the thigh or abdomen. The more sites you do, the more accurate the body fat percentage will be.
The 7 site measurements for men and women are the same. They are triceps, chest/pectoral, midaxillary (below the chest/ horizontal to the xiphoid process of the sternum), subscapular (back of the body between the spine and the bottom of the medial border of the scapular), suprailiac (on the side/above the hip bone, top portion of the curve of the pelvis), abdominal, & thigh.
How do I do take the measurements?
Now, when going over how to execute skinfold calipers, follow the step-by-step process below. I suggest that you have someone you trust perform it on you and to be considerate on their pinches (it can hurt!).
Steps (Applies to 3 and 7 site measurements)
At each site, use your thumb & index finger to grip the body fat
Once held, use the calipers to grab hold of the body fat
Grip the calipers so that it opens
1–2 cm away from the thumb & finger.
It should be perpendicular to the skin fold & halfway between the crest and the base of the fold
Release the caliper lever so that the tension goes onto the skinfold
Read the dial on the skin caliper (round to .5 mm & allow the number to equalize)
Take 2–3 measurements to find the average & repeat for each site
I have my numbers down, what’s next?
There's a 2-step process here. First, you must find the body density with the information you received from the calipers. Then from there, you use the body density and another equation to determine the body fat %.
The equation I use below is shared by (livestrong.com) and it is called the Jackson & Pollock equation for a 3-site measurement.
To calculate body density
For women, it is:
1.0994921 — (0.0009929 x the sum of the skinfold sites in millimeters) + (0.0000023 x the sum squared) — (0.0001392 x age) = Body Density
For men, its:
1.10938 — (0.0008267 x sum) + (0.0000016 x sum squared) — (0.0002574 x age)
That gives your body density. Then the BMI is calculated by using the equation below:
[(495/body density) — 450] * 100.
Below is an example of a 3-site equation using a 26-year-old man with a 20-millimeter chest, 22-millimeter abdominal, and 22-millimeter thigh measurement.
1.10938 — (0.0008267 x (20+22+22) + (0.0000016 x 4096) — (0.0002574 x 26) =Body Density
1.10938 — (0.0008267 x (64) + (0.0000016 x 4096) — (0.0002574 x 26) = Body Density
1.10938 — (.0529088) + (.0065536) — (0.0066924) = Body Density
Body Density = 1.0563324
Now that we have body density, let’s get percent body fat: The Siri equation (no not the phone assistant), is used here.
[(4.95/body density) — 4.5} x 100 = Body Fat %
[(4.95/1.0563324) — 4.5} x 100 = Body Fat %
[(4.686024967141025) — 4.5} x100 = Body Fat %
.186024967141025 x 100 = Body Fat %
18. 6024967141025 = Body Fat %
19% = Body Fat %
What’s Next?
Now that we have the approximated body fat percentage, you can now scroll up and look at the image with the different body fat percentages. You can see that the individual is within the healthy body fat percentage. If you are looking to do the 7-site fold, the same equation applies.
So, when it comes to which is more accurate between the 3 or 7 site measurements, it will be the 7-fold site since you have more numbers to add to the equation of figuring out your estimated BMI. Nonetheless, one of the cons here is that it will depend on the consistency of the skinfold grabs with the calipers. So, it is suggested to take several measures at each site (2–3).
2) Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) (Inbody)
What is BIA?
Bioimpedance analysis is a non-invasive, low cost, and commonly used approach for body composition measurements and assessment of clinical condition (inbodyusa.com). I’ve been exposed to the Inbody scale and it’s the one I’ve used in my time at corporate gyms. The way this system works is by sending a small electrical current into a person and measuring the opposition of the current as it travels throughout the body’s water (inbodyusa.com) Once this process is over you will get several numbers on the screen of the scale you’re using. Some of the data points that you get are Total body water, lean body mass, body fat mass, weight & body fat percentage.
Should I look at the BMI or PBF?
Regarding body fat percentage, the formula here is to divide the total body fat mass by total weight to get the percentage of body fat. This is my preferred method because of the fact that compared to BMI which is based on weight times height, it can be flawed. Say you have two young men. Same age, weight, and height. One is muscular and the other is on the obese side. They’d have the same BMI when the case is that the muscles young man are on a healthier side. See my point?
Now looking at the in-body analysis, it gives you both BMI & PBF while also showing you how much muscle mass you have. With all of the numbers, as you can see in the photo below, it’ll break it down in a bar graph so that you can know if you are under, over, or in a normal range of whichever parameter it is explaining. It’s a great machine, I love it and it is my recommended one!
So, one very important thing to know is that with the BIA, the data that you receive is based on:
The time
Where you are on an empty stomach or not
Properly hydrated
Rule of thumb
That’s just to name a few. Whenever you do weigh yourself, make sure the time and conditions are the same so that you can minimize the error in the numbers. While checking out your body composition, it is a great idea to take before photos. One general rule of thumb, especially when looking to change your body composition is that you may not necessarily drop pounds, yet you may look completely different. This is due to the fact of shedding body fat while increasing muscle mass. Totally normal and the photos that you take as progress, as well as the Inbody (BIA) would be able to show you this from a visual point and well as numerical. Make sure to be patient on your journey as the body transforms.
3) Tape measure
Now I saved a simple method for last in case you cannot get access to calipers or a BIA. This method will be similar to the calipers as the way in which you consistently record the numbers, will give you a more accurate measurement of body fat %.
How and what do I measure?
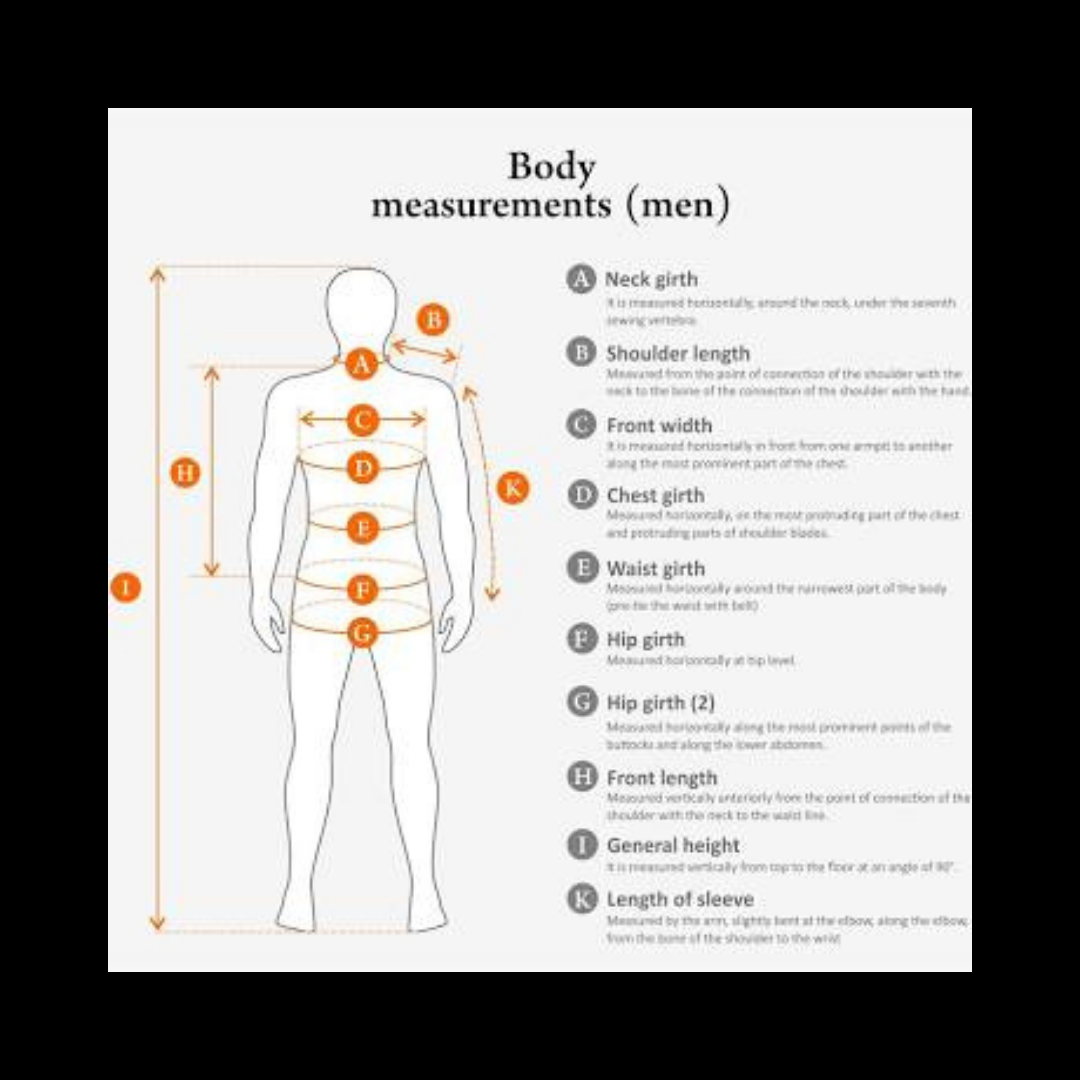
Ok, so I’ve included the areas for both men and women that you would need to record the measurement for. When measuring the, make sure that the tape is touching your skin, remove any slack that may appear as you are going around each body part. This part will be where the inaccuracy will show up. Take up to three measurements per body part.
Men & Female measurement requirements & sites
For men, the measurements you need to get are:
Neck
Abdomen
Measure your height.
For women,
Neck
Waist
Waist
Hips
Measure your height
Equations
Once you have gotten your measurements, now we will put them into a formula to get your body fat %.
Men
Body fat % = 86.010 log (abdomen — neck) — 70.041 log(height) + 36.76
Body fat % = 86.010 log (37–17) — 70.041 log (70) + 36.76
Body fat % = 86.010 log (20) — 70.041 log (70) + 36.76
Body fat % = 19.43
Women
Body fat % = 163.205 log (waist + hip — neck) — 97.684 log (height) — 78.387
Body fat % = 163.205 log (30 + 34–15) — 97.684 log (66) — 78.387
Body fat % = 163.205 log (49) — 97.684 log (66) — 78.387
Body fat % = 19.73
How can I do these calculations?
Now that you have the information know-how, make sure to use a scientific calculator (you can go on google, use your computers or download an app) so that you can do this equation and get as close to the accurate body fat %!
Hydrostatic Weighing
Hydrostatic weighing is a very precise measurement of body composition and is considered the gold standard, but it can be costly or hard to find. It measures body fat percentage by submerging the person underwater and getting them to exhale all their air. The change in buoyancy lets them measure the density of water displaced by the person's body. This changes with how hydrated you are, so you should always take your measurements in the same condition.
Whole Body Air Displacement Plethysmography (BODPOD)
The BODPOD is a very precise and clinical approach to measure your body composisitionmeasurement of body composition. It measures body fat percentage by sitting in a pod. Unline underwater weighing using water as the variable to do the body composition analysis, the body pod uses air to measure your body fat.
Dexa Scan
The Dexa Scan is a type of body scan. It uses low levels of radiation to determine the fat and muscle composition of the human body. The results are highly reliable and provide scientists with accurate data from various populations. The Dexa Scan is my gold standard and another clinical method of getting your body composition. The Princeton longevity center uses this in their executive physical examinations that few of my clients have done.
Some of the results that show up in the DEXA scan are the following
overall body fat, lean tissue (muscle), bone weight & percentages
breakdown of information for both legs, arms, and torso
Images showing where the body fat and muscle is distributed
Visceral fat
(information comes from DEXA Scan | Body Composition Test | Click Here For More Information)
Body Composition Takeaway
Body composition is one of the five health-related components of fitness. It is an indicator of how much body fat and muscle you have. You can find out your body fat percentage as well to see where you stand with your age group. You can use skinfolds, a tape measure, or a BIA (Inbody) to find out where you stand with your body composition. Percent of body fat is a better indicator than BMI. Out of the three methods mentioned, the BIA will have the highest accuracy, the skin calipers next, then the tape measure.
So, with this information gathered, you now can see if you are within a low, healthy, overweight, or obese range of body composition. With this knowledge, follow me to the next health component of fitness; cardiorespiratory endurance.
If you’d like to get into a program that helps you track your body composition while getting in shape, looking, and feeling great, join the 6-week training program below.